
What is geothermal energy and how do we use it?
Wells are being drilled into the earth to receive and re-inject hot water to return it to be energy.
In the form of naturally occurring steam and hot water, geothermal energy can be used to produce electricity, heat and cool buildings, and serve for many other uses which are explained in details on this site and around the internet.
Geothermal energy is a secure, environmentally sustainable, and cost-effective source of renewable energy that is growing in popularity across the world.
It is defined as energy in the form of heat stored beneath the surface of the Earth.
This heat can be found both near the surface and deep underground. In general, the deeper you go, the hotter it gets.
What are the benefits of using geothermal energy?
- It's clean energy which can be extracted and produced without burning any fossil fuels such as coal, gas, or oil.
- Using geothermal for electricity produces only about one-sixth of the carbon dioxide of a natural gas power plant, and little—if any—nitrous oxide or sulfur dioxide. Binary-cycle geothermal plants, which operate in a closed cycle, release essentially zero emissions.
- Geothermal sourcs are 100% countries own “free of charge” sources. It is national energy.
- Geothermal energy is available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, regardless of weather.
How does geothermal energy compare to other forms of energy?
- Geothermal energy is generally considered to be a clean and sustainable source of energy, with low greenhouse gas emissions and high efficiency. It is often compared to other renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power.
What are the benefits of using geothermal energy?
Yes, just like any other sources of renewable / green energy.
Geothermal plants don’t produce greenhouse gases, unlike conventional power plants that use fossil fuels like coal, oil, or gas.
Even though there might be some gas emissions from the ground (95% of which is carbon dioxide mixed into geothermal fluids), today’s technology makes it possible to contain the vast majority of these substances, preventing them from being released in the atmosphere.
According to a European Union report, every kilowatt-hour of geothermal energy saves 260 grams of CO2 compared to a gas-fired plant, 705 grams compared to an oil plant, and 860 grams compared to a coal-fired plant.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) calculated that 92 terawatt-hours of geothermal energy were produced worldwide in 2019; moreover, in the United States alone, geothermal plants are estimated to avoid the emission of greenhouse gases equal to 4.1 million tons of carbon dioxide a year.
Does geothermal energy help rural economies?
Yes, it does.
Many scientific studies confirm it: whether it is used to generate electricity or for heating, geothermal energy contributes to the development of rural economies and has positive impacts at a local level in the areas where the power plants are located.
The main benefits are social, industrial, economic and in terms of employment, and are particularly prominent in rural, mountainous, and remote areas.
Furthermore, geothermal energy can be used to heat agricultural greenhouses or aquaculture systems, as well as to provide power to industrial plants and heating systems.
When combined with other green energy sources, geothermal energy can generate even more substantial effects.
What kind of waste is generated by the construction of a geothermal plant?
Only once as digging the wells creates the most significant waste, because it generates drilling muds, soil, and rocks.
Recycling systems, non-polluting additives, and containment tanks are used to prevent ground contamination and reduce sludge production.
All the other kinds of waste (from packaging material to rubber and wood) are generated in very small quantities and the vast majority can be recycled like in any other houses and not more than that.
Even the various components of the power plant can be salvaged and reused at the end of their installation lifecycle.
How much noise does a geothermal system make?
When in full function, geothermal systems make a negligible amount of noise: large power plants emit as much noise as a vacuum cleaner, while home systems are significantly quieter. A certain amount of noise is inevitable during the construction phase (which includes subsurface exploration, drilling, and building), but once that is over everything goes quiet. This applies to both home systems and outside large power plants, which have a few turbines in motion at most.
How much space does a geothermal system take?
Unlike the wind turbines and solar panels, geothermal energy requires little space.
Whether it is a home system or a large-scale power plant, most of the components (including the heat exchangers) are underground, and very little remains above the surface.
A heat pump for a home is as big as a household appliance.
As for a power plant, the most imposing parts are the cooling towers, followed by the turbines.
Do geothermal plants emit unpleasant smells?
Infinitely less than in the past.
The unpleasant odor traditionally associated with geothermal energy and thermal water is due to the hydrogen sulfide (H2S) underground.
Nowadays, all power plants have an abatement system for hydrogen sulfide, which blocks around 99% of emissions thanks to its filters and containment technologies.
The small remaining part can be released into the air by the cooling towers, and rarely passes the odor detection threshold for even the most sensitive noses (set at 4 micrograms per cubic meter).
Larger concentrations are released only in case of exceptional circumstances and, even then, they still remain abundantly below the tolerable limit set by the World Health Organization (150 micrograms per cubic meter).
Does geothermal energy pose a risk to human health?
No, like in all other standard businesses, as long as all safety and mitigation measures are followed correctly.
Safety measures concern anything that could put power plant workers at risk.
What are the advantages of geothermal power?
Some advantages of geothermal power include its sustainability and consistency.
Geothermal energy is renewable, so it’s both more environmentally friendly and less susceptible to natural resource wars than fossil fuels are.
Geothermal can consistently produce energy output 24/7, regardless of weather conditions or seasonal changes.
How a geothermal well is drilled?
We reach a depth of more than three kilometres by using special drilling technology.
The drilling process of a well is a precise process requiring several weeks under the supervision of field professionals.
After transferring its energy, the extracted water cools down and is reinjected back into the reservoir through reinjection wells.
Can a geothermal well cause an earthquake?
Processes related to geothermal energy extraction are safe.
There is no connection for triggering an earthquake in geothermal well drilling or in geothermal well operaitons.
In order to earthquake to be started tremendous amount of energy must be affecting the ground which is not possible for humankind or by any well operation.
Do geothermal power plants and heating plants produce emissions?
Geothermal power plant or heating plant do not use conventional energy sources, thus produce just a minimum fraction of emissions.
Compared to fossil fuel facilities, geothermal produces 99 percent less carbon dioxide (just 0.63 kg per kilowatt hour of energy) and 97 percent less sulphuric compounds, which contribute to acid rain.
By proper reinjection, these emissions are reduced to zero.
This is also a reason why geothermal energy is considered an environmentally friendly resource.
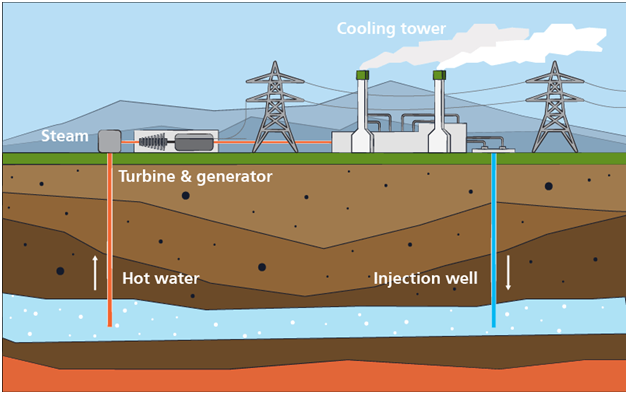
Geothermal General Drawing
How a Geothermal Power Plant Works.
FIRST WELLS ARE DRILLED TO REACH THE RESERVOIR
First of all, a production well is drilled into the reservoir. Along with that, an injection well is also drilled to return used geothermal water to the reservoir. Hot geothermal water runs in to power plant in order to produce electricity.
STEAM TURNS THE TURBINE
Hot geothermal water under pressure, or a secondary working used in the geothermal power plants, and or its steam runs through the tribunes to generate the electricity.
THEN THE TURBINE DRIVES THE ELECTRIC GENERATOR
As turbine shaft rotates it directly spins the magnets inside a large coil and create electrical current. The turbine and generator are the main items of the plant used to convert geothermal energy to electrical energy.
TRANSMISSION, POWER LINES DELIVER ELECTRICITY
Generated electric is then sent to a step-up transformer outside the power plant. Voltage is increased and set in the transformer and electrical current is transmitted over power lines to residential and commercial.

Sustainable

Cost-effective

Environmentally friendly

Renewable energy source
Low carbon energy families:
Geothermal has some of the most potential with the fewest drawbacks.
Solar panels are capable of generating power with zero emissions. The generated power can be used to feed your energy demand, perfectly replacing conventional energy needs with green energy. Every kilowatt of green energy can reduce your carbon footprint by 3,000 pounds annually.
Wind energy is a viable alternative of fossil fuels. It does not emit CO2 or other air pollutants. It runs virtually carbon free for its lifetime.
Reinjection
helps to maintain the pressure level in the reservoir. Another important benefit of reinjection is by continuous flushing of the rock matrix by the cooled water, the recoverable energy from the reservoir substantially increases.
Geothermal power
plants largely release only excess steam, with most plants discharging no air or liquid. This makes geothermal power plants a clean source of electricity and an important contributor to the nation's zero-carbon future.
Geothermal energy
is considered one of the most efficient and sustainable types of energy because it's a clean, reliable, and renewable resource. It uses the heat inside the earth's surface to generate electricity and provide heating and cooling.
Geothermal sources
are a renewable energy and will never deplete. Abundant geothermal energy will be available for as long as the Earth exists. It is a renewable energy source from the heat generated by the earth's internal core and is available 7/24/365.


