
Geothermal energy is generally considered to be a sustainable form of energy because it utilizes the heat energy stored beneath the Earth’s surface, which is a renewable resource. This means that as long as the Earth continues to produce heat, geothermal energy can be continuously generated without depleting any finite resources.
In addition, geothermal energy production emits very little greenhouse gases and other pollutants, making it a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels like coal and oil. While the construction of geothermal power plants can have some environmental impacts, such as land disturbance and noise pollution, these impacts are generally considered to be less severe than those associated with fossil fuel extraction and combustion.
Overall, geothermal energy is a promising form of renewable energy that has the potential to provide a significant source of electricity and heating in many regions of the world. However, as with any energy source, there are still some challenges and limitations associated with its implementation, such as high upfront costs and the need for appropriate geologic conditions for efficient production.
As the global population grows, demand for basic needs such as food, water, and energy rises as well, and this creates an increasingly vicious cycle where human activities adversely impact the environment and paradoxically threaten natural resources. In response to this phenomenon, nations around the world are seeking ways to break the cycle and to establish a more stable and secure future through sustainable practices in business and society.
There are certainly environmental advantages to using Geothermal technologies over conventional power generation.
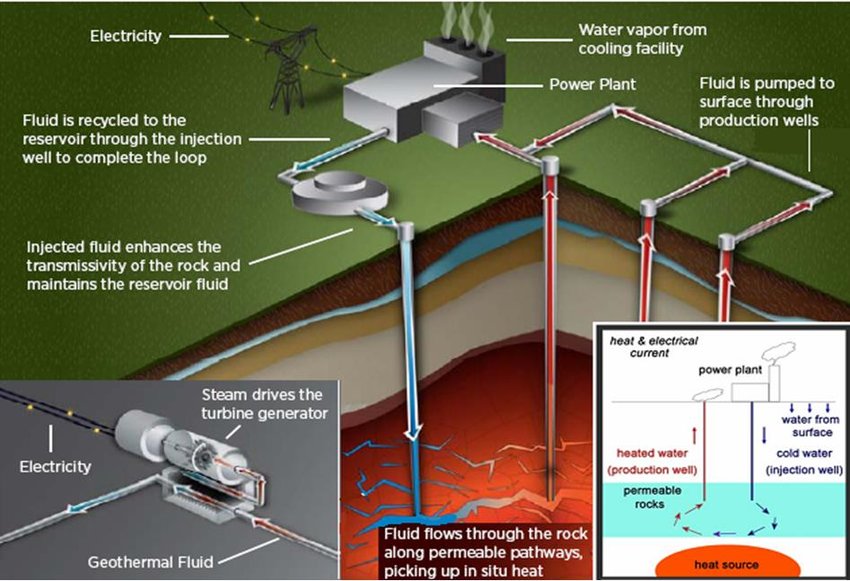
In order to extract power from geothermal energy, wells are dug deep underground to access the steam and hot water which can be used to drive turbines connected to electricity generators. There are three types of geothermal power plants: dry steam, flash, and binary. The binary geothermal power plant technology has no air or liquid emissions, only dry steam, making it the most favorable option of the three.
Geothermal energy is considered to be safe and sustainable because of the low carbon footprint and the vast amount of available heat generated and stored by the Earth’s core.
As the global population grows, demand for basic needs such as food, water, and energy rises as well, and this creates an increasingly vicious cycle where human activities adversely impact the environment and paradoxically threaten natural resources. In response to this phenomenon, nations around the world are seeking ways to break the cycle and to establish a more stable and secure future through sustainable practices in business and society.

Reinjection
helps to maintain the pressure level in the reservoir. Another important benefit of reinjection is by continuous flushing of the rock matrix by the cooled water, the recoverable energy from the reservoir substantially increases.
Geothermal power
plants largely release only excess steam, with most plants discharging no air or liquid. This makes geothermal power plants a clean source of electricity and an important contributor to the nation's zero-carbon future.
Geothermal energy
is considered one of the most efficient and sustainable types of energy because it's a clean, reliable, and renewable resource. It uses the heat inside the earth's surface to generate electricity and provide heating and cooling.
Geothermal sources
are a renewable energy and will never deplete. Abundant geothermal energy will be available for as long as the Earth exists. It is a renewable energy source from the heat generated by the earth's internal core and is available 7/24/365.
Low carbon energy families:
Geothermal has some of the most potential with the fewest drawbacks.
Solar panels are capable of generating power with zero emissions. The generated power can be used to feed your energy demand, perfectly replacing conventional energy needs with green energy. Every kilowatt of green energy can reduce your carbon footprint by 3,000 pounds annually.
Wind energy is a viable alternative of fossil fuels. It does not emit CO2 or other air pollutants. It runs virtually carbon free for its lifetime.

